In the UK, claiming business expenses correctly can have a significant impact on your company’s profitability. Understanding what expenses you can and cannot claim enables you to pay taxes only on your actual profits rather than on funds you’ve had to use to maintain your firm, regardless of whether you’re a shop owner, independent contractor, or the director of a limited company.
The regulations governing what is deductible can change based on your industry, ranging from office supplies and travel expenses to specialised equipment and professional services. Knowing these distinctions is important for more reasons than compliance; it’s important to ensure that you’re not losing money. We’ll break down typical and sector-specific company costs in this guide so you can reliably claim all of your entitlements and economically lower your tax liability.
Understanding Allowable Business Expenses in the UK
The charges you can subtract from your income when calculating your taxable profit are known as allowable business expenses. They must be “wholly and exclusively” for business objectives, meaning they must be directly related to operating your company. You can drastically cut your cost by claiming them, which lowers the amount of profit HMRC taxes.
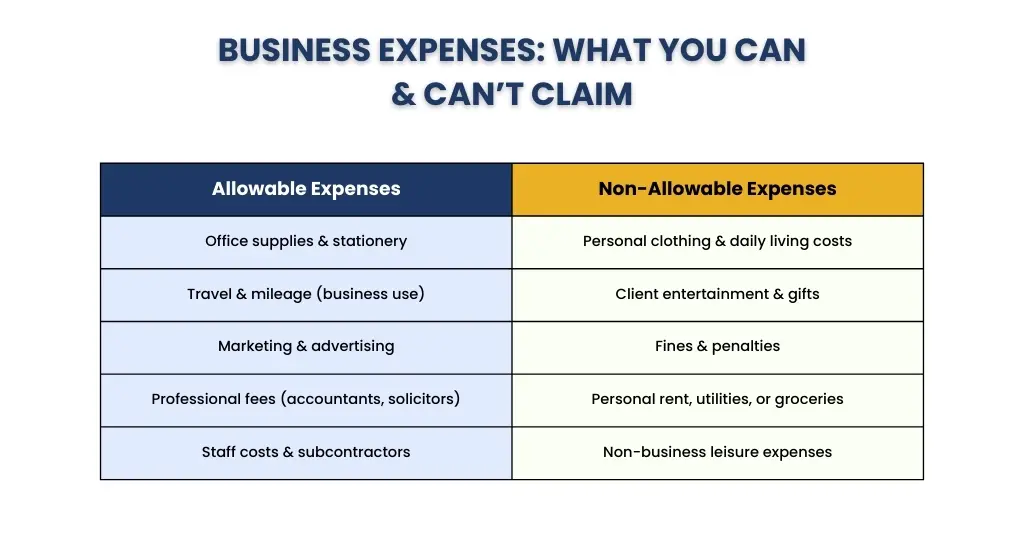
Allowable expenses include things like:
- Office costs (stationery, phone bills, internet)
- Travel for business purposes (mileage, public transport, accommodation)
- Staff wages and subcontractor payments
- Marketing and advertising costs
- Professional fees (accountants, solicitors)
- Utilities and rent for business premises
Non-allowable expenses, on the other hand, are costs that HMRC does not permit you to deduct — usually because they have a personal element or aren’t directly tied to your business activities. Examples include:
- Personal clothing (unless it’s protective or branded workwear)
- Client entertainment (meals, drinks, hospitality)
- Fines or penalties (e.g., parking tickets)
- Your salary (if you’re a sole trader)
- Personal living costs like rent, food, or leisure activities
Whether the expense is solely for company purposes or also involves personal benefit is the crucial difference. If the expense is a mix of both, you can only claim the business portion. Maintaining precise, thorough documentation is necessary to support these claims in case HMRC inquires.
Tax Reliefs on Business Expenses
Allowable business expenses are essentially an application for tax relief since they are subtracted from your income before taxes are calculated. This lowers your taxable profit and, thus, your tax liability.
For instance, HMRC would only tax you on £40,000 if your company makes £50,000 annually and you have £10,000 in permitted expenses. Utilising tax reliefs, you pay less tax (as long as you stay within the laws).
Different types of tax reliefs can apply depending on the nature of the expense:
- Capital allowances: Instead of paying a large sum of money for long-term assets like computers, machinery, or automobiles all at once, you can claim the full cost of these items using allowances like the Annual Investment Allowance (AIA) or Writing Down Allowance.
- Work-from-home allowance: If you work from home, you may be eligible to receive a fixed rate or a share of your household expenses.
- Mileage allowance: You can claim a certain amount per mile if you drive your personal vehicle for work purposes (45p for the first 10,000 miles, 25p for each additional mile).
- Research and Development (R&D) tax relief: Helps businesses to undertake eligible innovative activities, provide refundable tax credits or increased deductions.
What Are Allowable Expenses for the Self-Employed in the UK?
If you work for yourself, there are certain allowable expenses that you can claim to minimise your tax liability. These have to be costs directly relating to running your business, like buying supplies, travel costs, etc. A good practice is keeping the receipts in case HMRC asks to see them. By knowing what you can claim as a self-employed person in the UK, and understanding the best practices to ensure its legal utilisation, you can reduce your tax liabilities and keep more of your hard-earned money while staying fully compliant.

Industry-Specific Business Expenses You Can Claim
In the UK, certain charges are specific to each industry and might be considered legitimate company expenses. Being aware of these will help you keep more of your earnings and lower your tax bill.
eCommerce Business Expenses:
Website design and hosting, platform fees from websites like Amazon, eBay, or Shopify, payment processing fees like PayPal or Stripe, and advertising through social media or Google Ads are typical costs for eCommerce enterprises. Additionally, if you work from home, you can deduct some of your home office expenses, software subscriptions for analytics or inventory management, postage and packaging, and stock purchases. For the management of platform-specific fees, VAT on international sales, and stock write-downs, eCommerce accountants can be quite helpful.
Construction Business Expenses:
In the construction sector, acceptable expenses frequently include supplies like cement, timber, or fittings; protective gear and apparel; and tools and equipment (purchase, rental, or maintenance). The Construction Industry Scheme (CIS) allows for the deduction of payments to subcontractors, pertinent insurance policies, training and certification programs, and office or administrative expenses related to project management. In addition to assisting with capital allowances for heavy machinery and CIS deductions, construction accountants can help recover any unpaid taxes.
Restaurant Business Expenses:
The purchase and maintenance of kitchen equipment, employee salaries, uniforms, and food and drink supplies are all deductible expenses for restaurant enterprises. Along with marketing expenses like internet advertisements or menu printing, you can also deduct electricity, rent, and business rates for your space. Additionally eligible are supplies for cleaning and hygiene, maintenance and repairs, and music licenses for in-restaurant entertainment. Large transaction volumes, managing VAT on food sales, and maintaining strict control over operating expenses in a hectic setting are all tasks that restaurant accountants can assist with.
How to Keep Records and Claim Business Expenses Correctly
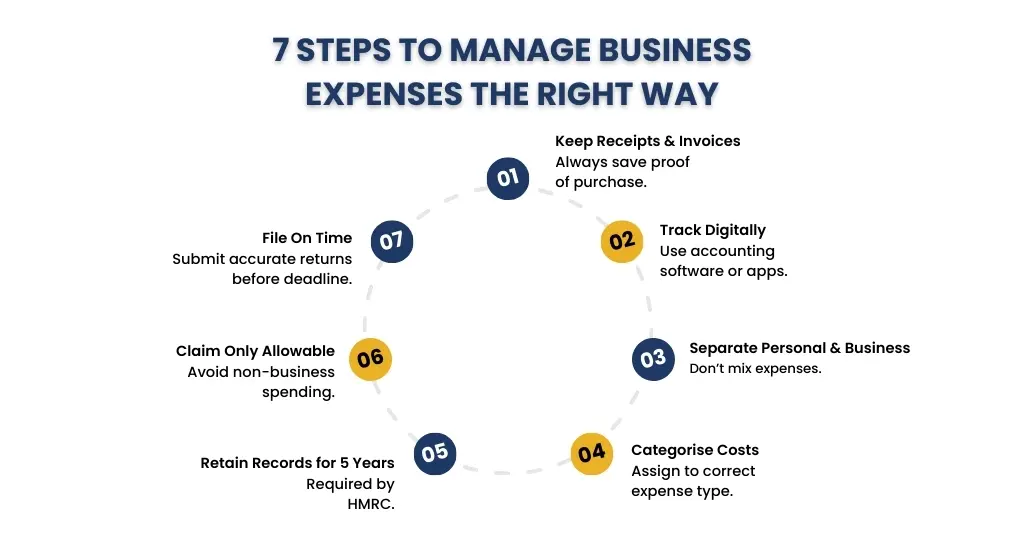
- Keep all receipts and invoices: Keep them digitally or physically, indicating the date, amount, and purpose of the business.
- Track expenses regularly: Spreadsheets or accounting software can be used to track expenses in real time.
- Separate personal and business costs: Only the business portion of expenses should be claimed for mixed-use expenses (such as phone and internet).
- Categorise expenses clearly: group costs into categories like travel, office, marketing, or equipment.
- Meet HMRC’s record-keeping rules: Maintain documentation for a minimum of five years following the deadline for filing taxes on January 31.
- Claim only allowable expenses: Make sure all expenses are used solely and completely for business.
- File accurately and on time: Submit tax returns correctly to avoid penalties and disallowed claims. Learn how dedicated tax accountants—such as those specialising in eCommerce—can help.
Need Help Claiming Business Expenses? E2E Can Help
It can be challenging to accurately claim business expenses, particularly when industry-specific regulations differ and HMRC requires thorough, precise documentation. We simplify the process at E2E. Our knowledgeable accountants assist you in maximising your tax savings, make sure your claims are compliant, and determine all of the permitted expenses to which you are entitled. Whether you manage a growing workforce, a limited company, or are self-employed, we will keep your records organised and your claims optimised so you can concentrate on managing your business while we take care of the statistics.
People Also Ask:
What can I claim as a business expense?
Expenses that are wholly and exclusively related to your business can be claimed, including office supplies, business travel, marketing, professional fees, equipment, stock, and some expenses related to your home office or car. It is not possible to claim personal or non-business expenses.
How do allowable expenses give you tax relief?
You receive tax relief through allowable expenses, which lower your taxable profit, the sum that HMRC uses to determine your tax liability. Since you only pay taxes on the amount that remains after deducting these expenses from your business income, you can keep a larger portion of your profits.
Can I claim lunch as a business expense?
Lunches are only deductible as business expenses if they are for business purposes, such as traveling for work or meeting a client somewhere other than your regular place of business. Lunch at your regular job or daily meals are not deductible expenses.
How much rent can I claim as business expenses?
You can claim the portion of your rent that relates to your business use as an allowable expense.
– You can typically claim the entire amount if you rent separate business space.
– Only the portion of rent that corresponds to the portion of the property occupied by your workspace and the amount of time spent on business purposes may be claimed if you work from home.
In order to avoid complicated calculations, HMRC also permits a simplified flat rate for working from home.

