In the UK, knowing how to avoid 40 tax UK can make a big difference for diligent workers in the construction and healthcare industries who frequently rely on contracts, overtime, or self-employment income to advance. Reaching the 40% tax level means a sizeable portion of your income is taken once your wages exceed £50,270 (as of the 2025–2026 tax year), leaving you with less for the future.
The good news is that there are clever and completely legal ways to lower your tax obligation without lowering your income. The tax system provides clever options that many professionals are just unaware of, regardless of your role, locum GP, agency nurse, contractor, or site manager.
You can work smarter, not harder, by following these five tried-and-true, HMRC-compliant techniques to keep more of your earnings.
Healthcare & Construction: Why They Hit the Higher Rate Tax Band Early
Professionals in healthcare and construction often find themselves in the 40% tax band sooner than they might expect, and not always because they’re making six-figure salaries. The main reason? Variable income.
In actuality, positions such as independent contractors, locum physicians, agency nurses, and self-employed craftsmen frequently earn variable compensation through project-based work, overtime, or shift rewards. It’s simple to surpass the £50,270 level without even realizing it, thanks to this erratic yet profitable arrangement, particularly if you’re not keeping a close eye on your tax situation. Computing for self employment tax accurately is very critical. .
A further contributing reason to this unintential tax liability and income fluctuation is the restricted utilisation of permitted deductions and reliefs, which frequently results from a lack of customised financial advice. A professional construction accountant or a medical finance advisor, sometimes referred to as a medical accountant, is trained to identify opportunities that lower your taxable income and increase your take-home salary, while a general accountant might not completely comprehend the complexity of these segments.
Without a tax strategy, you’ll hit the higher rate band sooner than you anticipate and may end up overpaying HMRC, regardless of whether you’re managing several contracts or balancing PAYE with self-employed work.
What is the 40% Tax Bracket?
In the United Kingdom, income tax is charged at a progressive rate, which means that the higher your income, the higher the tax rate on the percentage of your income that exceeds specific thresholds. Many professionals may not be aware that they have crossed the threshold, particularly those with variable incomes, such as construction contractors or healthcare locums.
Here’s a breakdown of the UK Tax Brackets 2025 for 2025/26 tax year (England, Wales & Northern Ireland):
| Tax Band | Income Range (£) | Tax Rate |
| Personal Allowance | Up to £12,570 | 0% |
| Basic Rate | £12,571 – £50,270 | 20% |
| Higher Rate | £50,271 – £125,140 | 40% |
| Additional Rate | Over £125,140 | 45% |
When you move into the higher-rate band, only the portion of your income over £50,270 is subject to 40% tax. However, it’s simple to lose thousands of dollars in needless taxes annually if you don’t plan.
Does the 40% Tax Bracket Ever Change?
The 40% tax bracket is subject to change. Income tax thresholds are reviewed by the UK government at fiscal events such as the yearly Budget. Modifications could consist of:
- Increasing or decreasing the threshold for the application of the 40% tax.
- By freezing the barrier, more incomes may eventually be forced into the upper band (a phenomenon known as fiscal drag). Imagine that while salaries gradually increase as a result of inflation, the higher-rate income tax threshold is fixed at £50,270 for several years.
- If Alex makes £48,000 in Year 1, the basic rate of tax is applied to all of their earnings.
- In Year 3, Alex’s pay has risen to £52,000, merely to keep up with growing living expenses rather than because they received a significant promotion.
Alex’s actual purchasing power hasn’t increased significantly, but a portion of their income now exceeds £50,270 and is subject to the higher 40% tax rate.
Additionally, UK self-employed tax changes, such as the introduction of IR35 reforms, can now impact how self-employed professionals are taxed, potentially pushing more individuals into the higher tax band if they’re not aware of the changes.
As of the 2025–2026 tax year, income between £50,271 and £125,140 is liable to the 40% rate; however, government action may alter this range.
5 Legal Strategies to Avoid Paying Higher-Rate Tax
You don’t have to accept that you’re in the 40% tax bracket. You may lower your taxable income and keep more of your earnings by using completely legal and HMRC-approved strategies. These five tried-and-true methods are frequently employed by both construction companies and medical specialists.
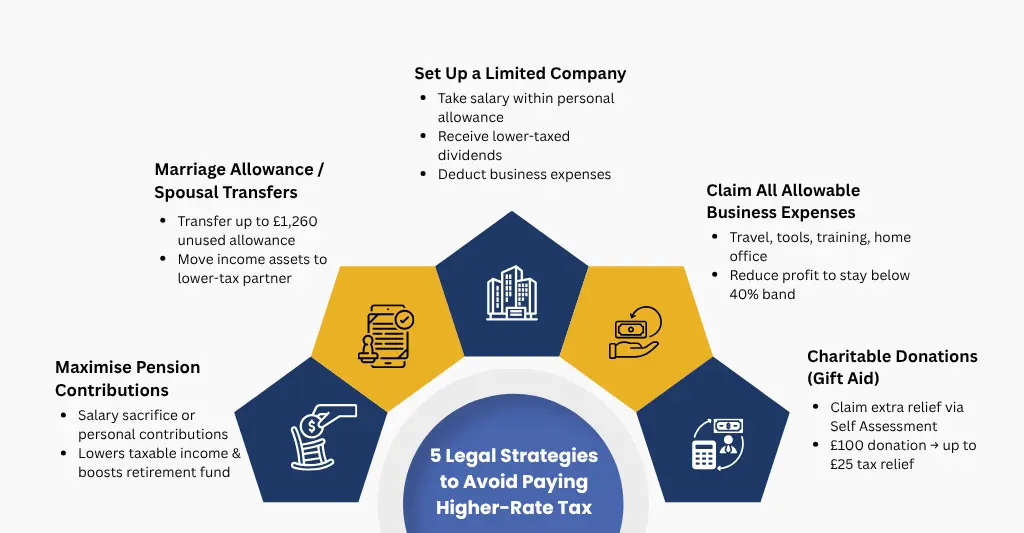
#1. Maximise Pension Contributions: One of the best strategies to reduce your taxable income is to contribute to a pension. You can help by:
- Salary sacrifice (via your employer)
- Personal pension contributions (if self-employed or working through a limited company)
These contributions help you stay below the 40% level and increase your retirement fund while lowering your income throughout the tax year.
#2. Use the Marriage Allowance or Spousal Transfers: In a civil partnership or marriage, you might be eligible to transfer up to £1,260 in unused Personal Allowance to a spouse who earns less than you do. This is known as the marriage allowance.
An alternative is to move income-generating assets (such as dividends or rental revenue) to your partner’s name if you’re a higher-rate taxpayer and they pay taxes at a reduced rate. This will lower your overall tax exposure. Consult an accountant at all times to make sure it’s done right.
#3. Set Up a Limited Company: Operating as a limited company might provide substantial tax benefits if you are an agency worker, locum, or subcontractor.
You can choose not to pay 40% income tax on all of your earnings by:
- Keep some of your income within the tax-free personal allowance (currently £12,570), so you don’t pay any income tax on that portion of your earnings.
- Receive dividends from your extra income, which are taxed at a reduced rate.
- Deduct company expenses from your profit.
You have more flexibility over when and how you’re taxed with this structure, particularly if your income varies.
#4. Claim All Allowable Business Expenses: Many independent contractors overpay taxes just by failing to report all of their allowable expenses. Among the allowed expenses are:
- Travel and mileage
- Tools, uniforms, or equipment
- Training and certifications
- Office or home-working costs
If you appropriately claim these, your taxable profit stays below the higher-rate band. Read our blog on Claiming Business Expenses for a detailed breakdown of what you can claim.
#5. Charitable Donations via Gift Aid: Gift Aid allows you to claim additional tax relief since HMRC treats the donation exactly like it were paid from taxed income when you use it to donate to a registered charity.
Taxpayers with higher rates can use Self Assessment to recover the difference between the basic rate (20%) and the higher rate (40%) on the amount given. If you donate £100, for instance, you may be eligible to get up to £25 in tax reduction.
If you want an in-depth guide on how to pay less tax, then read our blog – 7 legal strategies to pay less tax in UK
Important Tax Tip: Check for a Potential P800 Tax Refund
It’s not just about reducing your tax bill; it’s also about ensuring you’re not overpaying. If you’re a contractor or self-employed professional, tax codes can sometimes be incorrect, leading to overpayment. If HMRC identifies this, they’ll issue a P800 notice to let you know you’ve paid too much.
Checking for a P800 tax refund ensures you’re not missing out on money that should come back to you. If you’ve overpaid due to errors or a wrong tax code, the P800 is your way to reclaim it, reducing the impact on your overall tax situation.
Make sure you regularly check your tax code and keep track of any notices from HMRC. By staying on top of this, you’ll ensure you’re only paying the right amount and can avoid any surprises when tax time comes.
Bonus Tip: Monitor and Adjust Regularly
Tax planning calls for constant attention and is not a one-time event. You may stay below important thresholds like the £50,270 higher-rate band by routinely monitoring your wages, especially if you work overtime, have contracts, or are a freelancer.
Work with a professional medical or construction accountants, or utilise accounting software to:
- Track your income in real time
- Plan pension or charitable contributions before year end
- Identify opportunities for tax-saving adjustments
Being proactive will allow you to legally lower your tax liability before it becomes due, rather than after it is too late.
Conclusion
Even for high-earning professionals in the construction or healthcare industries, paying 40% tax is not certain. It is lawful to lower your tax burden while increasing your income if you have the correct information and take proactive measures.
Every tactic listed above, from maximising pension contributions to forming a limited business, complies completely with HMRC regulations and may be modified to fit your work arrangement, whether you’re self-employed, contracting, or PAYE with extra income. For guidance on selecting the right setup for your situation, see our blog on choosing a business structure.
The secret is to act quickly and to periodically assess your position. Working with a specialised accountant who is aware of the particular prospects and difficulties in your sector is even better.
People Also Ask:
Do I really need to pay 40% tax in the UK?
Only if your taxable income in 2025–2026 is more than £50,270. However, by employing strategies like business expenses, pension contributions, or limited company formation, you can legally decrease or avoid paying 40% tax, so with careful preparation, you might not have to pay it at all.
What is the 40% tax bracket in the UK?
The higher-rate tax band, or 40% tax bracket, applies to taxable income between £50,271 and £125,140 (for the 2025–2026 tax year). You pay 40% income tax on earnings in this range after deducting your personal allowance.
Is the 40% tax rate applied to all my income?
No, only the part of your income over £50,270 is subject to the 40% tax rate. Only the amount in the higher-rate band is subject to 40% tax; income below that is subject to lower rates of 20% or 0%.
Example:
If you earn £55,000 in a year:
– The first £12,570 is tax-free (personal allowance).
– The next £37,700 (£50,270 – £12,570) is taxed at 20%.
0 Only the final £4,730 (£55,000 – £50,270) is taxed at 40%.
So you don’t suddenly pay 40% on your whole salary, just on the slice above the higher-rate threshold.
When do I start paying 40% tax?
In the UK, you start paying 40% income tax once your earnings exceed the £50,270 threshold. Thus, its important to keep track of your income and accounts, and precisely deduct allowable expenses.
How to legally pay less tax in the UK?
You can legally reduce your tax bill in the UK by using HMRC-approved methods such as:
– Contributing to a pension (salary sacrifice or personal)
– Claiming all allowable business expenses
– Donating to charity through Gift Aid
– Using the Marriage Allowance or spousal transfers
– Operating through a limited company (if self-employed or contracting)
These strategies lower your taxable income, helping you stay out of higher tax brackets. Know in-detail by going through our blog – How to Pay Less Tax in UK
What are the UK tax brackets for 2025 (25-26 tax year)?
Personal Allowance: Up to £12,570 (0%)
Basic Rate: £12,571 to £50,270 (20%)
Higher Rate: £50,271 to £125,140 (40%)
Additional Rate: Over £125,140 (45%)

